MongoDB uses unicode, instead of the coding
for a certain local language, to sort data in this language (i.e. Chinese).
Together with esProc, MongoDB can realize sorting in local language
conveniently (i.e. sort Chinese according to Chinese phonetic alphabet). The
following will teach you the method in detail by taking Chinese as an example.
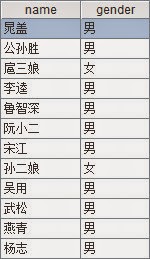
person - a collection in MongoDB - stores names and genders as follows:
>
db.person.find()
{
"_id" : ObjectId("544e4e070f03ad39eb2bf498"),
"name" : "宋江", "gender" : "男"}
{
"_id" : ObjectId("544e4e070f03ad39eb2bf499"),
"name" : "李逵", "gender" : "男"}
{
"_id" : ObjectId("544e4e070f03ad39eb2bf49a"),
"name" : "吴用", "gender" : "男"}
{
"_id" : ObjectId("544e4e070f03ad39eb2bf49b"),
"name" : "晁盖", "gender" : "男"}
{
"_id" : ObjectId("544e4e070f03ad39eb2bf49c"),
"name" : "公孙胜", "gender" : "男" }
{
"_id" : ObjectId("544e4e070f03ad39eb2bf49d"),
"name" : "鲁智深", "gender" : "男" }
{
"_id" : ObjectId("544e4e070f03ad39eb2bf49e"),
"name" : "武松", "gender" : "男"}
{
"_id" : ObjectId("544e4e070f03ad39eb2bf49f"),
"name" : "阮小二", "gender" : "男" }
{
"_id" : ObjectId("544e4e070f03ad39eb2bf4a1"),
"name" : "孙二娘", "gender" : "女" }
{
"_id" : ObjectId("544e4e070f03ad39eb2bf4a2"),
"name" : "扈三娘", "gender" : "女" }
{
"_id" : ObjectId("544e4e080f03ad39eb2bf4a3"),
"name" : "燕青", "gender" : "男"}
…
Sort the data using MongoDB’s sort function rather than the Chinese
phonetic alphabet:
>
db.person.find({},{"name":1,"gender":1,"_id":0}).sort({"name":1})
{
"name" : "公孙胜", "gender" : "男" }
{
"name" : "吴用", "gender" : "男" }
{
"name" : "孙二娘", "gender" : "女" }
{
"name" : "宋江", "gender" : "男" }
{
"name" : "扈三娘", "gender" : "女" }
{
"name" : "晁盖", "gender" : "男" }
{
"name" : "李逵", "gender" : "男" }
{
"name" : "杨志", "gender" : "男" }
{
"name" : "武松", "gender" : "男" }
{
"name" : "燕青", "gender" : "男" }
{
"name" : "阮小二", "gender" : "男" }
{
"name" : "鲁智深", "gender" : "男" }
…
The esProc script helping with MongoDB computation
is as follows:
A1:Connect to the MongoDB database. The IP and port number
is localhost:27017, the database name
is test and both the user name and
the password are test. If any other
parameters are needed, write them in line with the format mongo://ip:port/db?arg=value&…
A2:Fetch data from the
MongoDB database using find function
to create a cursor. The collection is person. The filtering criterion is null
and the specified keys are name and gender. It can be seen that this find function is similar to the find function of MongoDB. By fetching
and processing data in batches, the esProc cursor can avoid the memory overflow
caused by big data importing.
A3:Since the data here
are small, fetch function will fetch
them all at once.
A4:Sort the data by name in ascending order, using sort function. Chinese is used in the data
sorting. For the other localized languages esProc supports, please see below.
One thing to note is that esProc doesn't
provide the java driver of MongoDB. To access MongoDB with esProc, the latter
(a driver of 2.12.2 version or above is required, i.e. mongo-java-driver-2.12.2.jar)
should be put into the [esProc installation directory]\common\jdbc beforehand.
The script for computation in MongoDB with the
assistance of esProc is easy to integrate with Java program. By adding another
line of code – A5, which is result A4,
the result in the form of resultset
can be output to Java program. For detailed code, please refer to esProc Tutorial. In the same way, to
access MongoDB by calling esProc code with Java program also requires putting
the java driver of MongoDB into the classpath of Java program.
The java driver of MongoDB can be
downloaded from the following URL: https://github.com/mongodb/mongo-java-driver/releases.


No comments:
Post a Comment